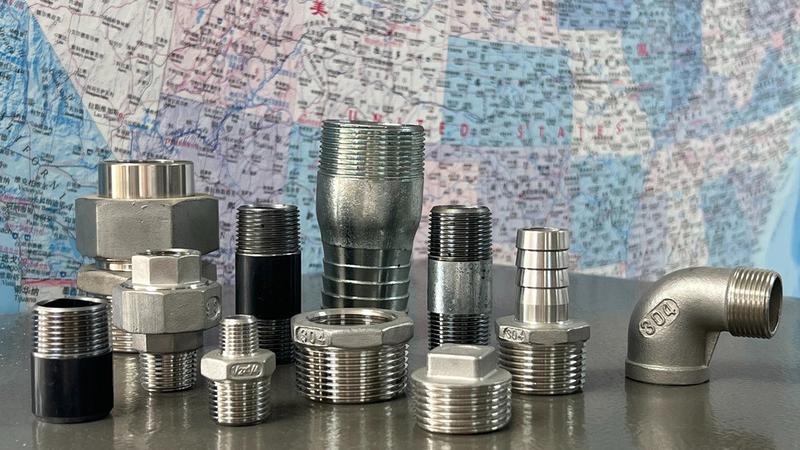
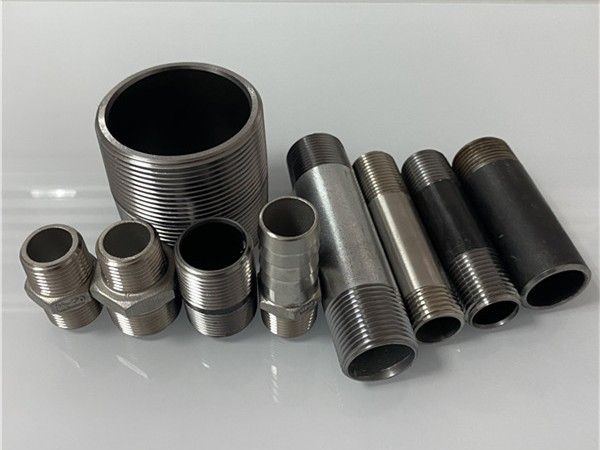
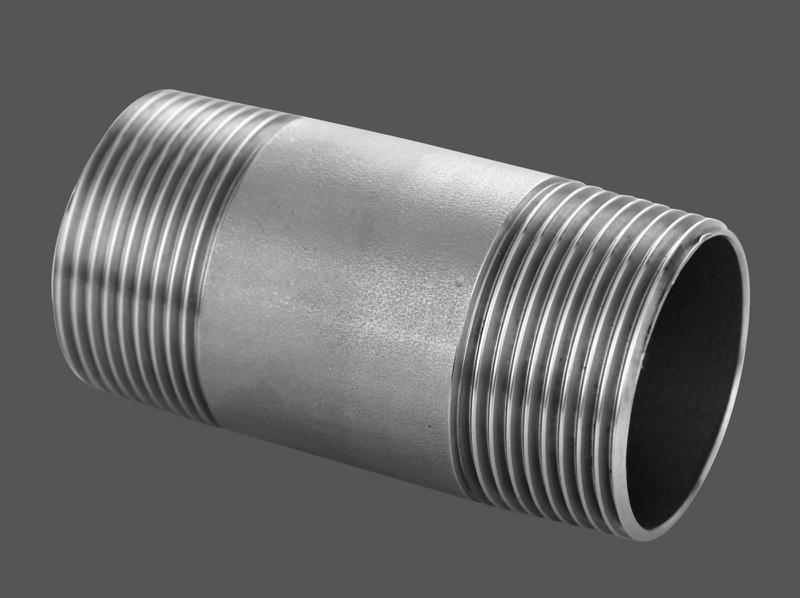
What Is a Male Thread?
A male thread is an externally threaded component designed to screw into a corresponding female thread (internal thread). Male threads are commonly used in industrial plumbing, gas, oil, and water systems to create NPT, BSP, and metric threads for high-pressure and corrosion-resistant male threaded applications.
Key Features:
-
Connect other female thread pipes or fittings through their male threads
-
The wide variety includes pipe nipples (short pipes with male threads on both ends), hex nipples, plugs, street elbows, male adapters, and more.
-
Materials: stainless steel or carbon steel
Critical Industries
-
Oil and gas
-
Chemical processing
-
HVAC systems
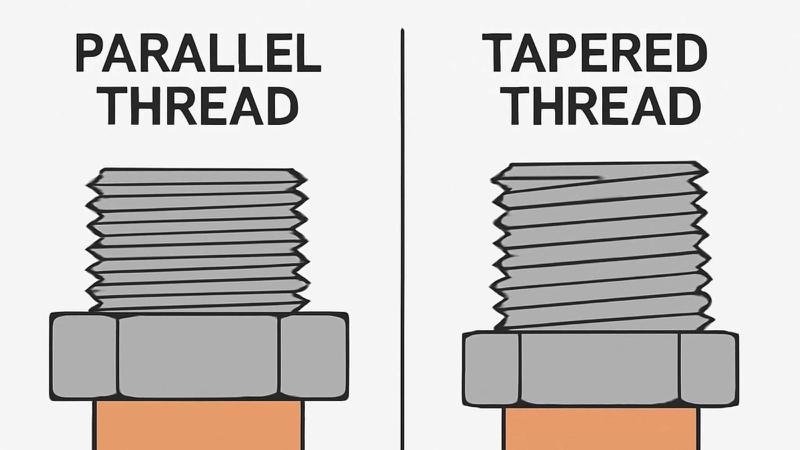
Parallel Thread vs. Tapered Thread
Parallel Threads (e.g., BSPP)
-
Design: Consistent diameter across the thread.
-
Applications: Low-pressure systems requiring gaskets or seals.
-
Pros: Easy assembly, reusable.
Tapered Threads (e.g., NPT, BSPT)
-
Design: Diameter decreases toward the end.
-
Applications: High-pressure systems (self-sealing via thread deformation).
-
Pros: Leak-resistant without additional sealants.
| Feature | Parallel Thread | Tapered Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | Moderate | High |
| Sealing Method | Gasket/O-ring | Thread deformation |
| Common Uses | Hydraulic couplings | Gas pipelines |
How to Select the Right Male Plumbing Fittings
-
Pressure Requirements: Tapered threads for systems exceeding 1,000 PSI.
-
Material Compatibility: Stainless steel for corrosive environments.
-
Thread Standards: Match regional norms (e.g., NPT in North America).