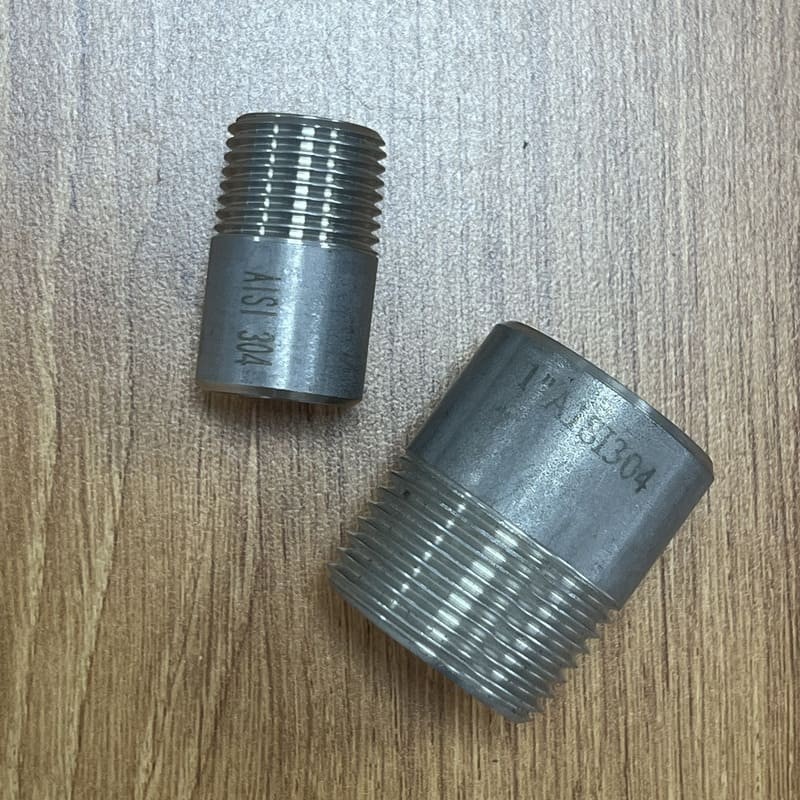
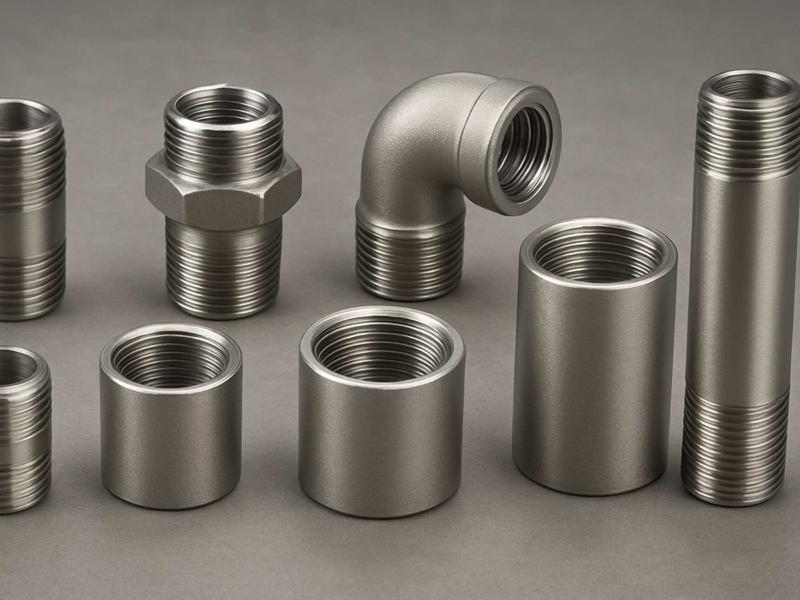
What are Forged Fittings?
Forged fittings are pipe connectors produced through the metal forging process, in which metal is shaped under high temperature and pressure.
This process refines the grain structure of the material, eliminates internal voids, and creates a dense, high-strength structure with excellent mechanical performance.
What is the Difference Between Forged Fittings and Cast Fittings?
The main difference between forged fittings and cast fittings is in their production processes. Forged fittings are produced by heating metal to a high temperature and shaping it under pressure using forging and pressing equipment. In contrast, cast fittings are created by pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify.
The forging process produces fittings with a high-density structure and excellent strength, while cast fittings are more prone to air holes or inclusions due to their lower density.
Forged fittings generally have a smoother surface and lighter weight, while cast fittings are rougher in appearance and heavier due to their solidified casting structure.
In the oil, gas, high-pressure steam system, chemical industry, shipbuilding, power plants, high corrosion, high temperature environment and other applications, forging fittings such industry's first choice, can play its own maximum advantage; and casting fittings do not have to be used in this kind of extreme application environment, the most commonly used in the low-pressure water pipes and drainage systems.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
| Property | Forged Fittings | Cast Fittings |
| Strength | High. Tensile strength and toughness are better | Lower |
| Density | High | Low, easily formed pores |
| Impact resistance | Excellent | General |
| Service life | Long | Relatively short |
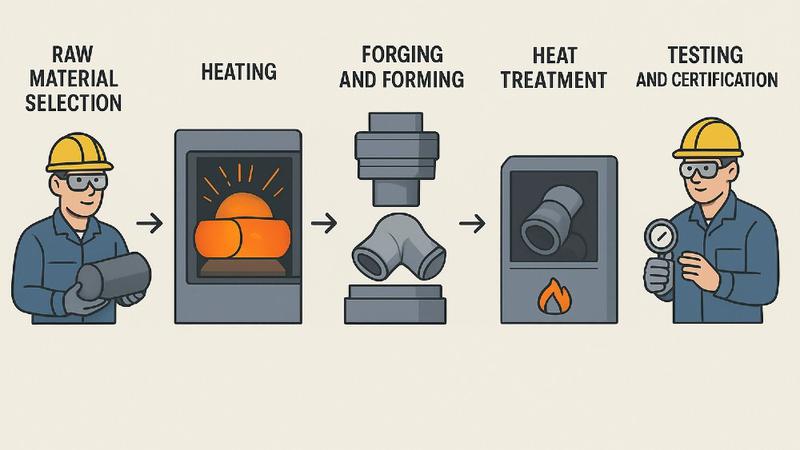
Forged Fitting Manufacturing Process
-
Raw Material Selection: Carbon or stainless steel (e.g., ASTM A105, A182) is typically used.
-
Heating: The billet is heated to a plasticized state at a high temperature.
-
Forging and forming: By die forging or free forging, the material is pressed into the required shape (e.g., elbow, tee, socket, etc.).
-
Heat treatment: including normalizing, annealing, quenching, tempering, and other processes to improve the organization and properties.
-
Machining: Threading, beveling, and finish processing.
- Testing and Certification: Conduct dimensional, strength, pressure, hydrostatic, and flaw detection tests, and comply with ASME/ANSI/ASTM standards.
Forged Fittings Types
Carbon steel fittings (Galvanized or Black Coated): pipe nipples, pipe couplings
Stainless steel fittings: pipe nipples, pipe couplings, pipe elbows, pipe tees, pipe caps, pipe unions, pipe plug, hex bushing, hex nut, pipe cross, valves, flanges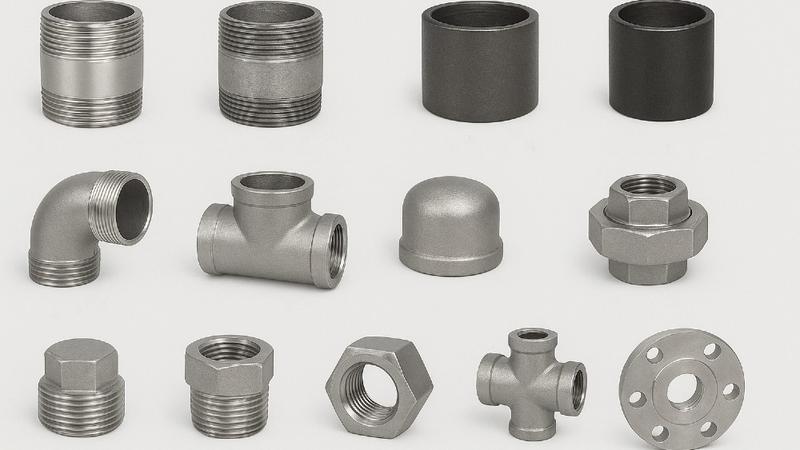
Common Standards for Forged Fittings
Our factory produces forged fittings with carbon steel and stainless steel.
Carbon steel generally adheres to the ASTM A105 standard. In contrast, stainless steel follows the ASTM A182 standard, each defining the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment requirements for different types of steel used in forged fittings.
ASTM A105 – Carbon Steel Forged Fittings
ASTM A105 is the standard specification for carbon steel forgings used in piping components such as pipe nipples and couplings for ambient- and high-temperature services.
Material type: Plain carbon steel
Applications: Oil and gas pipelines, power generation, and petrochemical plants
Characteristics:
Excellent strength and toughness under pressure
Good machinability and weldability
Can be supplied with black or galvanized coating for enhanced corrosion resistance
Typical products: Welded and threaded pipe nipples, couplings
ASTM A182 – Stainless Steel Forged Fittings
ASTM A182 covers forged stainless steel fittings, flanges, valves, and parts for high-temperature or corrosive service.
Material type: Austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, or duplex stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316)
Applications: Chemical processing, food and beverage, shipbuilding, power plants, and offshore industries
Characteristics:
Superior corrosion and oxidation resistance
Suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature environments
Excellent surface finish and dimensional stability
Typical products: Pipe nipples, couplings, elbows, tees, unions, caps, plugs, crosses, and flanges
FAQ
1. Q: What is the Relationship between ASME & ASTM standards?
A: ASTM defines material properties, while ASME (e.g., ASME B16.11) defines dimensions, pressure ratings, and design tolerances.
2. Q: What are the Pressure Ratings of Forged Fittings?
A: Common pressure classes: 2000, 3000, 6000, and 9000.
3. Q: What are the Connection Types of these Pipe Fittings?
A: Socket Weld and Threaded (NPT/BSP).
4. Q: What of the Surface Treatment of Carbon Steel Fittings can I select?
A: Black phosphate or black sandblasted coated and electroplated or hot-dipped zinc coating.





