Pipe schedule is a pipe wall thickness grade, a numbering system used to represent a series of steel pipe wall thicknesses, formulated by the ASME/ANSI standard.
The pipe schedule does not indicate a material or pressure grade, but a wall thickness series number.
Definition of Pipe Schedule
Pipe schedule = Wall Thickness Number
The higher the pipe schedule number, the thicker its wall. A thicker wall allows the pipe to withstand higher pressure.
Pipe schedule commonly includes:
-
SCH 10 (thin wall)
-
SCH 20
-
SCH 40 (medium wall thickness, most common)
-
SCH 80 (thick wall)
- SCH 160 (ultra-thick wall)
What is Schedule 40?
Schedule 40 steel pipe refers to a standard specification for the wall thickness of steel pipes. This specification is defined by ASME/ANSI B36.10M and B36.19M.
Schedule 40 is the most commonly and widely used medium wall thickness grade.
Does SCH 40 equal the Pressure Grade?
No. It can influence the pressure grade, but does not directly express the pressure grade.
The true pressure grades must correspond to the material sizes (such as A53, A106, and API 5L), temperatures, wall thickness, and standards.
Characteristics of Schedule 40 Steel Pipes
Medium wall thickness allows steel pipes to withstand medium pressure.
Sch 40 steel pipe is widely used in water systems, gas, low-pressure steam, and general industrial piping systems.
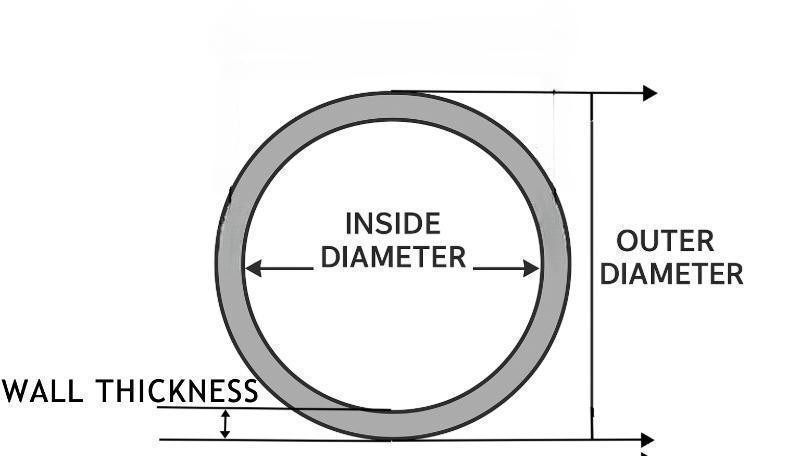
The wall thickness varies with different sizes; SCH 40 is not a fixed measurement but changes depending on the pipe diameter.
But the same schedule in the different nominal pipe sizes, the pipe wall is different, such as the schedule 40 pipe thickness:

| Pipe Schedule | NPS | Wall Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| SCH 40 | 1" | 3.38 mm |
| 2" | 3.91 mm | |
| 4" | 6.02 mm |
Compare Pipe Schedule 20 vs 40 vs 80 vs 160
"Pipe Schedule" indicates the grade of pipe wall thickness. The larger the number, the thicker the wall thickness and the stronger the pressure resistance.
-
Wall thickness comparison
SCH 20 < SCH 40 < SCH 80 < SCH 160
-
Wall Thickness Differences
Take NPS 2" (2 inches) as an example:
| NPS | Schedule | Wall Thickness (mm) | Wall Thickness Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2" | SCH 20 | 2.11 mm | Thin Wall |
| SCH 40 | 3.91 mm | Medium | |
| SCH 80 | 5.54 mm | Thick Wall | |
| SCH 160 | 9.53 mm | Extra Thick |
-
Trend of pressure resistance capacity
Under the same material and size, the pressure resistance capacity increases with the wall thickness
SCH 160 > SCH 80 > SCH 40 > SCH 20
SCH 40 has a medium wall thickness compared to SCH 10, SCH 80, and SCH 160.
| NPS | DN | Outside Diameter (in) / (mm) (ASME) | Nominal Wall Thickness | |||
| SCH 20 (mm) | SCH 40 (mm) | SCH 80 (mm) | SCH 160 (mm) | |||
| 1/8″ | 6 | 0.405 in (≈ 10.3 mm) | — | 1.73 mm | 2.41 mm | — |
| 1/4″ | 8 | 0.540 in (≈ 13.7 mm) | — | 2.24 mm | 3.02 mm | — |
| 3/8″ | 10 | 0.675 in (≈ 17.1 mm) | — | 2.31 mm | 3.20 mm | — |
| 1/2″ | 15 | 0.840 in (≈ 21.3 mm) | — | 2.77 mm | 3.73 mm | 4.78 mm |
| 3/4″ | 20 | 1.050 in (≈ 26.7 mm) | — | 3.91 mm | 5.56 mm | 7.82 mm |
| 1″ | 25 | 1.315 in (≈ 33.4 mm) | — | 3.38 mm | 4.55 mm | 6.35 mm |
| 1¼″ | 32 | 1.660 in (≈ 42.2 mm) | — | 3.56 mm | 4.85 mm | 6.35 mm |
| 1½″ | 40 | 1.900 in (≈ 48.3 mm) | — | 3.68 mm | 5.08 mm | 7.14 mm |
| 2″ | 50 | 2.375 in (≈ 60.3 mm) | — | 3.91 mm | 5.54 mm | 8.74 mm |
| 2½″ | 65 | 2.875 in (≈ 73.0 mm) | — | 5.16 mm | 7.01 mm | 9.53 mm |
| 3″ | 80 | 3.500 in (≈ 88.9 mm) | — | 5.49 mm | 7.62 mm | 11.13 mm |
| 4″ | 100 | 4.500 in (≈ 114.3 mm) | — | 6.02 mm | 8.56 mm | 11.11 mm |
| 6″ | 150 | 6.625 in (≈ 168.3mm) | 7.11 mm | 7.11 mm | 10.97 mm | 14.27 mm |
| 8″ | 200 | 8.625 in (≈ 219.1 mm) | 8.18 mm | 8.18 mm | 12.70 mm | 18.26 mm |
| 10″ | 250 | 10.750 in (≈ 273 mm) | 9.27 mm | 9.27 mm | 12.70 mm | 21.44 mm |
| 12″ | 300 | 12.750 in (≈ 324 mm) | 10.31 mm | 10.31 mm | 12.70 mm | 25.40 mm |
Compare Key Features when Choosing Pipes
-
Wall Thickness
Pipe wall thickness is the key difference; the essence of the schedule is the grade of the wall thickness.
-
Pressure Rating
The primary purpose of different pipe schedules is to accommodate various pressure requirements.
The larger pipe schedule allows the pipe to withstand higher pressure with the same pipe material and size.
-
Pipe Weight
The pipe schedule is smaller, and the pipe weight is lighter.
The weight of the pipe affects transportation and installation costs, as well as the structural load requirements.
-
Cost
A thicker pipe contains more material, making it more expensive.
Conclusion
Pipe schedule is a wall thickness designation system; higher schedule numbers mean thicker walls.
When selecting suitable pipes, pay close attention to wall thickness, pressure rating, pipe weight, and cost—these are the 4 key features.
About Us
SANVO is a leading manufacturer and supplier of high-quality pipe fittings, steel pipes, and customized metal components, serving the global market.
Our product range includes threaded fittings and welded fittings, such as couplings, elbows, tees, and reducers. We can manufacture according to your exact dimensions, materials, and project requirements.
Visit our facilities or contact our team to experience efficient, customer-focused service.